比赛地址
D. Edge Weight Assignment
题意
给出一棵树,每条边可以赋予一个任意大小的正边权,最终要满足任意两个叶子节点间的路径上的所有边权的异或值为0.定义f为这棵树上不同边权的数量,求f的最值.
题解
首先如果某个节点上连出了很多个叶子,显然有该点到这些叶子的边权都是相同的,那么可以把这些叶子缩成一个叶子.设缩点完成后树的大小为m.则f的最大值即为m-1.
最大值的证明比较简单.首先选取任意一个非叶子节点作为根.用类似树上DP的思路自底向上给边赋值.因为缩完点的缘故,树的形状类似一个鱼骨(见下图).可以给最深的那个叶子连接的那条边赋值为2^{n}-1,n趋向于无穷大.然后自底向上赋值即可.
官方题解是选择了一个叶子为根,然后自上向下赋值,大体的赋值思路是一样的,参考下图:
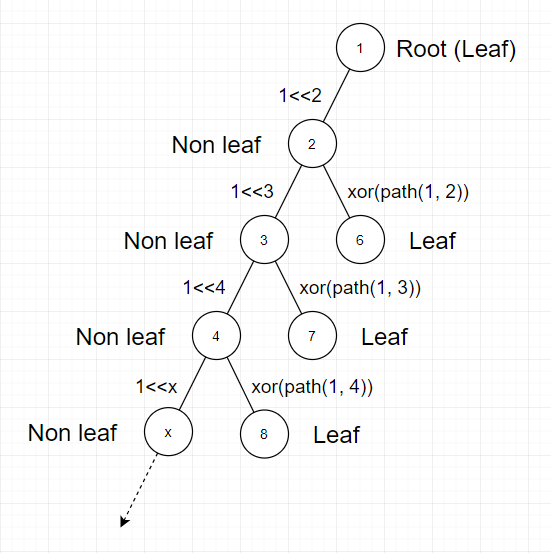
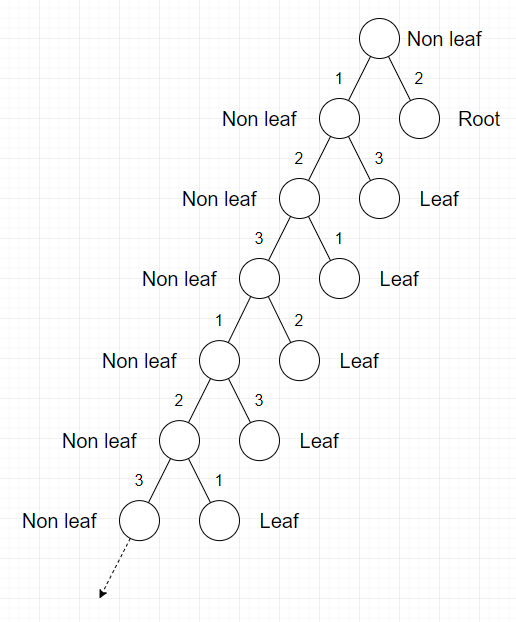
最小值稍微简单一些.比赛时通过样例盲猜最小值要么是1,要么是3.当且仅当任意两个叶子间的距离为偶数时答案为1,否则为3.可以只使用1,2,3这三个数完成赋值,思路见下图:
代码
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#define l(x) (x<<1)
#define r(x) ((x<<1)+1)
#define IL inline
#define reg register
#define LL long long
#define N 400010
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
int n,i,x,y,lsum=1,root,tot,Ans1,Ans2;
int head[N],f[N],size[N],d[N],p[N],l[N],g[N],o[N];
vector <int> son[N];
map <int,int> M;
struct Edge{
int t,next,l;
}e[N*8];
IL int Find(int x){return (x==p[x])?x:p[x]=Find(p[x]);}
inline void Add(int s,int t){
e[lsum].t=t; e[lsum].next=head[s]; head[s]=lsum++;
}
IL int Abs(int x){return (x<0)?-x:x;}
IL void Swap(int &a,int &b){a^=b^=a^=b;}
IL int Min(int a,int b){return (a<b)?a:b;}
IL int Max(int a,int b){return (a>b)?a:b;}
IL int read(){
int p=0,f=1; char c=getchar();
while (c<48||c>57) {if (c=='-') f=-1; c=getchar();}
while (c>=48&&c<=57) p=(p<<1)+(p<<3)+c-48,c=getchar();
return p*f;
}
IL void Maketree(int x,int fa){
int i=0;
size[x]=1;
// cout<<x<<" "<<fa<<endl;
for (i=head[x];i;i=e[i].next){
if (e[i].t==fa) continue;
f[e[i].t]=x; son[x].push_back(e[i].t);
Maketree(e[i].t,x);
size[x]+=size[e[i].t];
}
}
IL void Dfs(int x){
if (!son[x].size()){
o[p[x]]=1; return;
}
for (auto i : son[x]){
Dfs(i);
g[p[x]]+=o[p[i]];
o[p[x]]+=g[p[i]];
}
if (g[p[x]] && o[p[x]]) Ans1=3;
}
int main(){
#ifdef __Marvolo
freopen("zht.in","r",stdin);
freopen("zht.out","w",stdout);
#endif
n=read();
for (i=1;i<n;i++){
x=read(); y=read();
Add(x,y); Add(y,x);
d[x]++; d[y]++;
}
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
if (d[i]>1) {
root=i;
break;
}
Maketree(root,0);
for (i=1;i<=n;i++) p[i]=n+i;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
if (!son[i].size())
p[i]=p[f[i]];
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
if (p[i]==n+i) p[i]=i;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
if (!M[p[i]]) Ans2++,M[p[i]]++;
Ans1=1;
Dfs(root);
/* for (i=1;i<=n;i++){
for (auto j : son[i])
printf("%d ",p[j]);
putchar(10);
}*/
printf("%d %d\n",Ans1,Ans2-1);
return 0;
}
E. Perfect Triples
题意
有一个正整数集合S,刚开始S为空.然后需要从所有不在S的正整数中选出字典序最小的三元组,使得a \oplus b \oplus c=0.然后把这三个数依次加到S中,再继续寻找三个数,不断重复以上过程.添加到S中的数按照加入的顺序构成了一个无穷长的序列,求这个序列某一位的值.
题解
打表找规律(因为OEIS上没搜到这个数列)
如果把这个数列每三位归为一组,很多组又会构成一个有规律的小节.每一个小节的第一组打头的数的规律是:1,4,16,64...每一个小节内部,打头的第一个数依次递增.每一个小节的长度刚好也是1,4,16,64...接下来以小节为单位,研究第二个数的出现规律.
假如说某个小节的第一个数的范围是[ a , 2a-1 ],那么第二位的数的范围是[2a,3a-1].整个小节内部又均分成四部分,每一个部分打头的数是2a,2a+\frac{2a}{4},2a+\frac{3a}{4},2a+\frac{a}{4}.每一部分的第二位数又按照同样的规律分布,类似于自相似图形,直接DFS算就行了.第三位数可以通过前两位数推出,问题解决.
官方题解使用了数学归纳法,归纳每个小节内部的数恰好为[4^{n},4^{n+1}-1].第一位数按照[4^{n},2\times4^{n}-1]从小到大排列.第二位数的规律可以用下表概括:
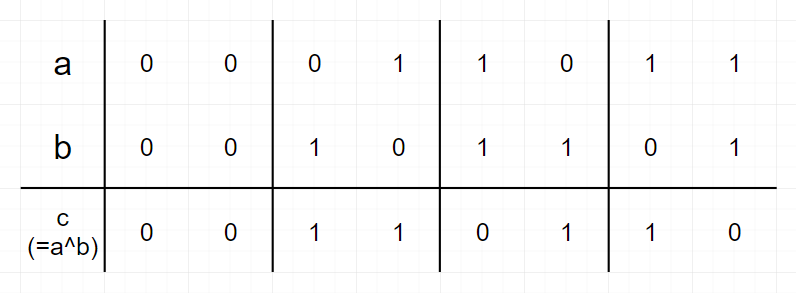
解释了上面打表找到的规律.剩下归纳的部分就很容易完成了.
题解评论区中有人给出了第二位数的OEIS地址
代码
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#define l(x) (x<<1)
#define r(x) ((x<<1)+1)
#define IL inline
#define reg register
#define LL long long
#define N 100010
#define M 700
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
LL i,j,k,T,n;
IL int Abs(int x){return (x<0)?-x:x;}
IL void Swap(int &a,int &b){a^=b^=a^=b;}
IL int Min(int a,int b){return (a<b)?a:b;}
IL int Max(int a,int b){return (a>b)?a:b;}
IL LL read(){
LL p=0,f=1; char c=getchar();
while (c<48||c>57) {if (c=='-') f=-1; c=getchar();}
while (c>=48&&c<=57) p=(p<<1)+(p<<3)+c-48,c=getchar();
return p*f;
}
IL LL Find(LL x,LL l,LL r,LL len){
if (len==0) return l+(x-1);
if (x<=len) return Find(x,l,l+len-1,len/4);
else if (x<=2*len) return Find(x-len,l+2*len,l+3*len-1,len/4);
else if (x<=3*len) return Find(x-2*len,l+3*len,l+4*len-1,len/4);
else return Find(x-3*len,l+len,l+2*len-1,len/4);
}
IL void Cal(){
LL i=0,d=1,l=3,p=0,q=0;
if (n<=3){
printf("%I64d\n",n);
return;
}
while (n>l){
n-=l; d*=4; l*=4;
}
l=d+(n-1)/3;
q=Find((n+2)/3,2*d,3*d-1,d/4);
if (n%3==1)
printf("%I64d\n",l);
else
if (n%3==2)
printf("%I64d\n",q);
else
printf("%I64d\n",l^q);
}
int main(){
#ifdef __Marvolo
freopen("zht.in","r",stdin);
freopen("zht.out","w",stdout);
#endif
T=read();
while (T--){
n=read();
Cal();
}
/*v[1]=v[2]=v[3]=v[4]=v[5]=v[8]=v[10]=v[12]=v[15]=1;
T=50;
while (T--){
for (i=1;i<=M;i++)
for (j=i+1;j<=M;j++)
for (k=j+1;k<=M;k++){
if (v[i] || v[j] || v[k]) continue;
if ((i^j^k)!=0) continue;
printf("%d %d %d\n",i,j,k);
v[i]=v[j]=v[k]=1;
goto END;
}
END:;
}*/
return 0;
}
本文地址: Codeforces Div2 633 部分题解

